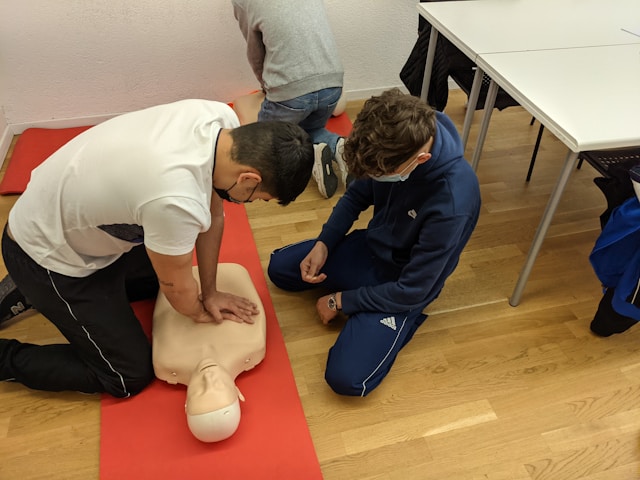
When providing medical care, the procedure you decide to perform can heavily influence whether you save them. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation or CPR is an emergency treatment for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest incidents. There are multiple techniques, with hands-only and traditional CPR being the most popular.
The Importance Of CPR
CPR is critical to mitigating common heart failures. It’s ideal to bring people with these experiences to a medical facility. With equipment like oxygen concentrators and defibrillators, they can administer oxygen and stop abnormal heart rhythms.
Unfortunately, these attacks don’t always happen in or near these health centers. About 356,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur annually, with almost 90% of them fatal. If a loved one ever has an emergency, you must perform CPR.
Hands-Only CPR vs Traditional CPR
Hands-only chest compressions begin by placing one hand’s heel onto the victim’s center. The rescuer should pump hard and fast for at least two inches deep, following a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. This action aims to keep the vital organs alive by distributing the remaining oxygen in the heart.
Traditional CPR combines the same set of chest compressions with rescue breaths. For every set of 30 compressions, the rescuer must tilt back the victim’s head, pinch their nose closed, and provide two breaths through the mouth. This method provides an extra supply of oxygen to go through the body.
Hands-only and traditional CPR are both effective for emergency services and mitigating cardiac arrest. The former is ideal if the victim may have remaining oxygen. However, if a rescuer is uncertain whether they have oxygen left, it’s recommended to do CPR with breaths instead.
Hands-only CPR is also recommended if a rescuer is squeamish or conscious about mouth-to-mouth contact. Chest compressions can still help victims recover from cardiac arrest, so it’s much better than doing nothing.
Factors to Consider
Choosing between hands-only and traditional CPR is relatively situational. Here are the factors you must consider when deciding what technique to perform.
Age
The age of a cardiac arrest victim is quite influential on their oxygen levels. Adults and teens are pretty standard, making hands-only CPR quite viable. However, infants, children, and older people may benefit more from traditional CPR.
Younger and older age groups have a higher oxygen demand than the rest of the pack. Their body’s oxygen production and consumption may not be fully developed or is deteriorating, which makes CPR with breaths crucial.
Health Condition
A victim’s health condition can also be an influential factor. For example, piling on frustration constantly and going through stressful situations can result in heart failure. People with stress-induced conditions may get by with hands-only CPR.
Panic attacks can drain their oxygen supply, so traditional CPR is much more effective. This technique is more effective for those dealing with pregnancy. However, it’s vital to note the risk of disease transmission. Rescuers are encouraged to take formal CPR training to learn more.
Causes
The cause behind the cardiac arrest can influence what form of CPR to give. People who are drowning or have gone through a drug overdose may have limited oxygen supply. As a result, rescue breaths are paramount to save them.
In some cases, hands-only CPR is an alternative, primarily focused on whether the mouth is accessible for ventilation. The victim should always be flipped on their back on a firm, flat surface to perform CPR. However, their mouth may be unavailable due to injury.
Length and Reaction
Cardiac arrest can seem to happen instantaneously, but it can take a while. However, death can occur within minutes without treatment, which makes it even more urgent. Chest compressions are critical for the first few minutes of heart arrest to ensure survival. It’s recommended that you contact emergency services at this time.
The chest should recoil between compressions as the victim showcases signs of life. If this happens, the rescuer is at a good stopping point. However, if the victim is unresponsive, it’s ideal to switch from hands-only CPR to traditional instead. The chest should rise with each breath for maximum effectiveness. Perform the cycles repeatedly until help arrives.
Perform the Right Form of CPR
Hands-only and traditional CPR are both beneficial yet different techniques. To verify the ideal method, look for factors in a cardiac arrest incident. Choosing the right one and properly performing it can save a loved one.
Mia Barnes
More from Mia Barnes
5 Tips for Students Interested In The Medical Field In The Age Of COVID-19
Read More
You may also like

Birth Control: What Method Is Right For You?

Celiac Disease Versus Gluten Intolerance: 6 Things To Know

What Does Your Health Need From You This Year?